|
Back to Topics<<<< If the passage of the meal or faecal masses is affected, it is called obstruction. It is of two types: 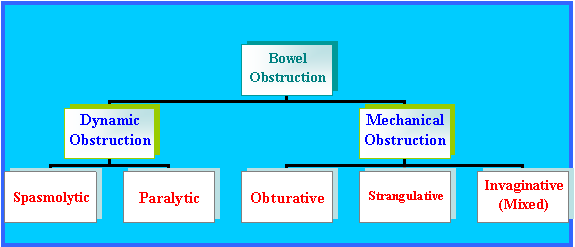 Dynamic Obstruction: Nerve fibres innervate the bowels such as Meissener’s (submucosal) and Aurebach’s (myenteric) plexus. Heavy meals such as mercury, arsenic etc. have their toxic effects on these plexuses and as a result, spasmolytic obstruction occurs. In this type of obstruction, there is no organic block but there is functional obstruction as the intestines fail to transmit peristaltic waves. Paralytic type of ileus occurs when there is some inflammatory process in abdominal cavity (appendicitis), due to its toxic effect on neuromuscular mechanism. Mechanical Obstruction:
X-Ray examination with or without barium contrast reveals inverted cups so called Clubber’s cups. Treatment:
Surgery is done by the resection of the affected area. First we take the proximal tube and create a stoma through muscular layer. Then we connect this loop to a bag temporarily for the excretion of the faecal masses. After sometime (4-6 months) when the inflammatory process is decreased, then we make the proximal and distal end anastomosis. This is called Hartmann type of operation. Hartmann performed this operation in 1921 due to tumour obstruction. In small bowels we can make end to end anastomosis without creating any stomas. This article has been written by Dr. M. Javed Abbas. If you have any comments please do not hesitate to sign my Guest Book. 21:04 21/12/2002 |